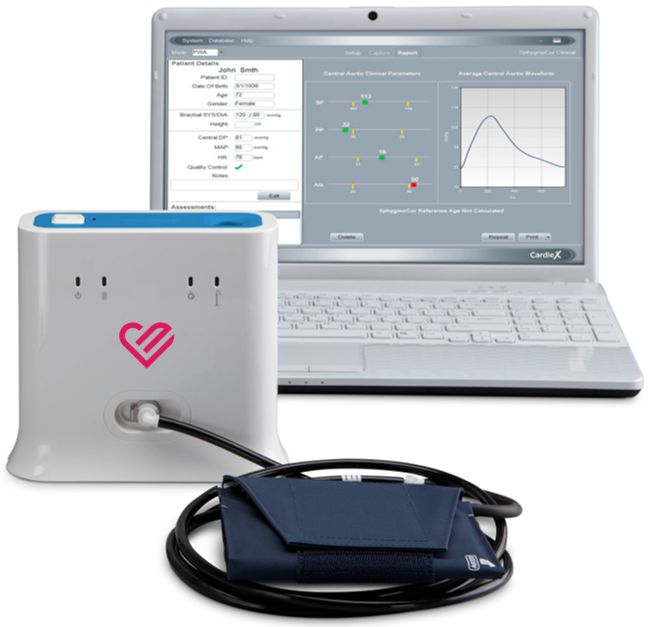
An Atcor Medical SphygmoCor device was used to monitor central and brachial blood pressure systolic mean and diastolic during rests of the strength maneuvers. Validation of non-invasive central blood pressure devices.
Technologies Free Full Text Cuff Less And Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring A Methodological Review Html
Overall the prevalence rates of ISH isolated diastolic hypertension.

Central blood pressure device. Higher central blood pressures mean that the heart must work harder to do its job. First cuff devices are familiar in clinical practice promoting the easy-use of cBP. Central and brachial BP were simultaneously measured using a cuffbased standalone central blood pressure monitor purporting to measure invasive central BP type II device.
This is the pressure in the arteries when the heart rests between beats. Devices that purport to measure central blood pressure BP should undergo rigorous testing for accuracy validation by comparison to invasive central aortic BP. Measurement of cBP from upper-arm cuff brachial-based oscillometric devices instead of classical tonometry methods is more attractive for three further reasons.
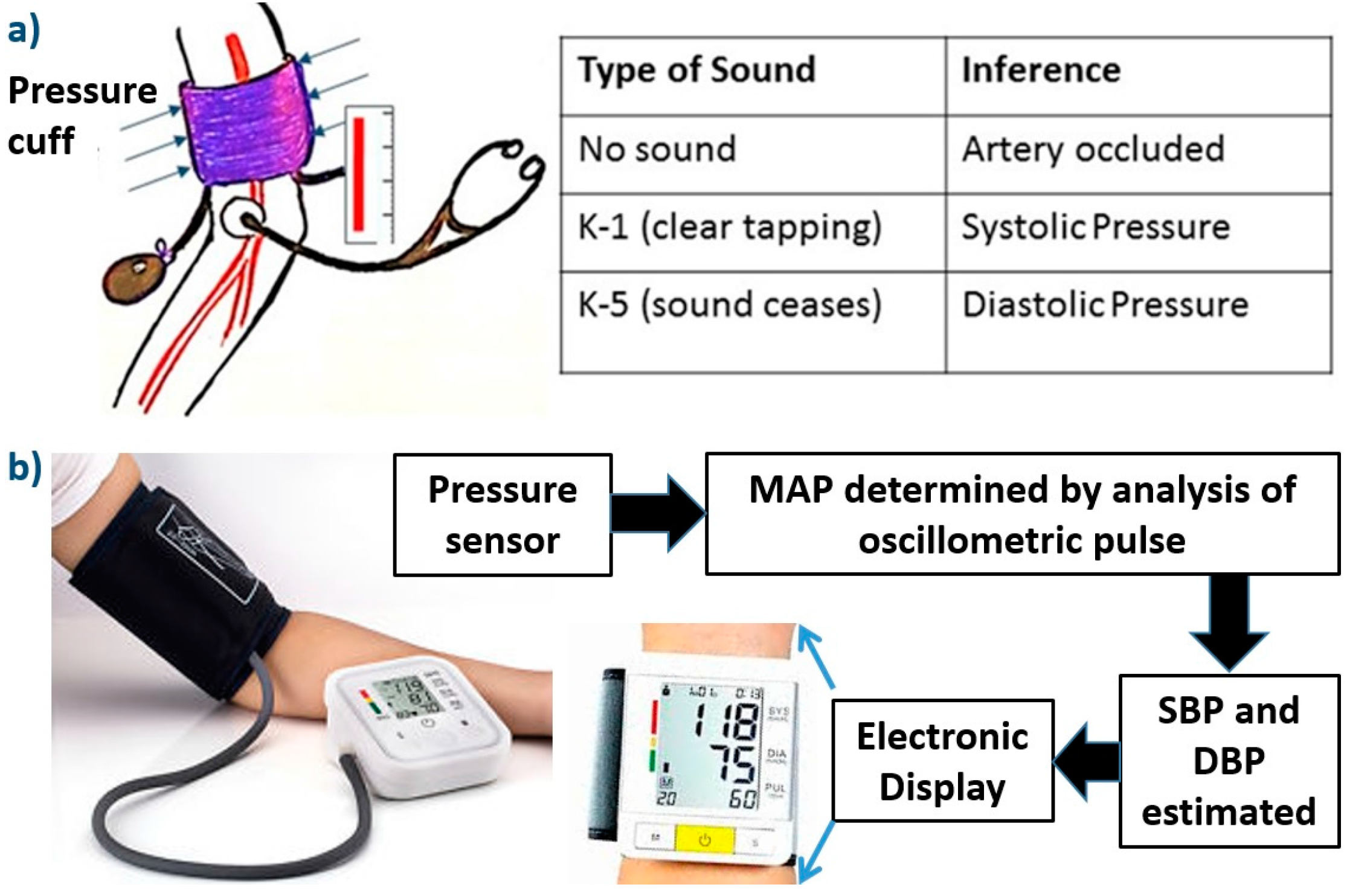
The point where blood begins to intermittently flow through the brachial artery is recorded as the systolic blood pressure the top number The point when the flow goes from intermittent to a continuous flow is the diastolic blood pressure the bottom number. Within the cuff is a sensor that can detect blood flow. 59 Zeilen Since noninvasive central blood pressure BP measuring devices are readily.
The tonometer is placed on the skin over the brachial artery in the arm. Central blood pressure waveform is recorded at the carotid artery level direct method. There have been advances in recent years including the proposal of novel methods and commercialization of several.
Here we describe the design and operation of an ultrasonic device that is conformal to the skin and capable of capturing blood-pressure waveforms at deeply embedded arterial and venous sites. What is Central Blood Pressure. Numerous factors such as arterial stiffness affect the pressure wave as it travels.
Central aortic pressure CAP is a potential surrogate of brachial blood pressure in both clinical practice and routine health screening. One method of measuring central blood pressure is with a tonometer a small instrument shaped like a wand. Mobil-O-Graph ambulatory blood pressure monitor device which automatically measure pulse wave velocity PWV central blood pressure cBP augmentation index Aix and central pulse pressure cPP was used to evaluate arterial stiffness.
It is the pressure that the target organs are exposed to and due to arterial pressure amplification is lower than brachial cuff pressures. The wearable device is ultrathin 240 μm and stretchable with strains up to 60 and enables the non-invasive continuous and accurate monitoring of cardiovascular events from multiple body locations. The patch works by emitting continuous ultrasound waves that monitor subtle real-time changes in the shape and size of pulsing blood vessels which indicate rises or drops in pressure.
Noninvasive measurement of CAP becomes a crucial technique of great interest. Central blood pressure is the pressure that the heart has to pump against to get blood to flow to the rest of the body. Arterial pulse wave is recorded at the radial artery level after which.
Deep Dive into Noninvasive Central Blood Pressure NcBP Central blood pressureor cBPcan be measured directly with a sensor-enabled catheter inserted directly into the ascending aorta the main arterial blood vessel from the heart. The second number is the diastolic pressure. Central hypertension was defined by central systolic SBPdiastolic BP DBP 130 or 90 mm Hg and ISH was defined by brachial SBP 140 and DBP 90 mm Hg.
In this study estimated central BP by the SphygmoCor Xcel cuffbased device was compared to invasive central aortic BP using multiple calibration methods. Second these devices are suitable for 24-h ambulatory BP monitoring. Central Blood Pressure is the pressure in the ascending aorta just outside the left ventricle.
An ultrasonic and stretchable device conformal to the skin that captures blood pressure waveforms at deeply embedded arterial and venous sites enables the continuous monitoring of cardiovascular. However this procedure is risky because its invasive and expensive because its risky and is usually only performed on critically ill patients in acute care. This can eventually lead to heart failure.
Pulse transit time was estimated from ECG and BCG recordings and simultaneously recorded with all BP readings. Central blood pressure also determines the pressure in the blood vessels feeding the brain. If central pressure is too high it may cause aneurysms and strokes.
It directly reflects the status of the central aorta. Third these devices measure the peripheral waveform and BP for waveform calibration. Blood pressure taken at the arm is called peripheral blood pressure How is central blood pressure measured.
Blood pressure is not a constant force throughout the body. As described recently in Nature Biomedical Engineering when this small patch is worn on the neck it measures blood pressure way down in the central arteries and veins more than an inch beneath the skin 1. ARTERY Society task force consensus statement on protocol standardization Eur Heart J.

Noninvasive Methods Of Central Blood Pressure Measurement Download Table

Central Blood Pressure And Its Clinical Implications
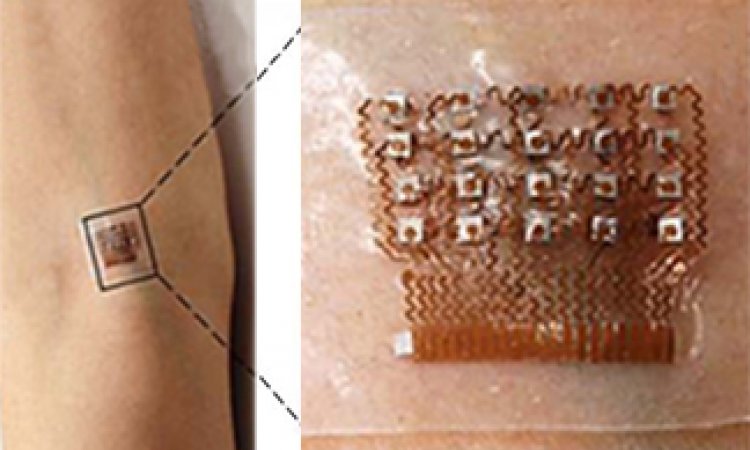
Wearable Ultrasound Patch Penetrates The Skin To Measure Blood Pressure